Types of Brainwaves
Types of Brainwaves are important to know cause Our brain is an electro-chemical organ. We can measure the electrical output of our brain using EEG (also called a brain map or QEEG). Science has discovered that certain high and low electrical activity is associated with specific neurobehavioral symptoms. EEG has been used for many years to determine seizure activity and proof of life. We use this advanced technology to determine the quality of one’s life and function in the patients we serve.
brief descriptions of each type of brain wave and Types of Brainwaves:
Delta (1-4 hertz): Often referred to as the sleep wave. High delta waves are not a bad thing when we are asleep. High delta waves in a wakeful state can be very problematic. Brain fog is associated with high levels of delta waves. Brain fog in adults can show up as losing keys, not remembering where you parked, asking others where you left off mid-sentence, or forgetting appointments. Brain fog in children is usually seen when they zone out and have a hard time staying on task.
Theta (4-7 hertz): Referred to as the focus and attention wave. Also called the meditative wave. High Theta waves have been associated with attention deficit disorder for many years. We often see high Theta with autism cases, ADHD cases, and people in their 40s and 50s who can longer focus well.
Alpha (8-12 hertz): We refer to alpha waves as the emotional waves. People who make high alpha tend to have difficulty controlling their emotions. They may experience mood swings, anger, and many have short fuses. High alpha can also make it difficult for us to filter our environment. People who make low alpha waves tend to experience more depressive states and/or low motivation.
Beta (13-30 hertz): Beta is associated with executive functions. These include learning, communication, understanding, prioritizing, task initiation and completion, organization, and managing new situations. Unbalanced beta waves are associated with many different issues, including forms of ADHD and Autism Spectrum. High beta can also be seen in anxiety, OCD/addiction, fatigue, memory problems, chronic pain, and insomnia. Low beta is often seen in low function brains and people who are experiencing burnout.
We can use a tool called neurofeedback to balance these brain waves. Neurofeedback is the retraining of brain waves using a computerized monitoring and reward system. A patient sits and watches a movie while photic (light) stimulation suggests to the brain to speed up or slow down, depending on the case. When the brain does what we want, the patient is rewarded by the computer with being able to see and hear a movie for instance. When the brain goes back to the old, negative pattern, the movie fades out and mutes. This process of reward teaches the brain how to create better connections. By this process, a feedback loop is created. This allows the patient’s brain to learn how to regulate the brain waves by itself through a process known as NeuroPlasticity. The process often takes between 20-40 sessions to complete. Like learning to ride a bicycle, the results can last for many years, barring any head trauma or major psychological trauma.
Neurofeedback enjoys a high success rate for many neurobehavioral symptoms. We blend the neurofeedback model with advanced neurologic rehab activities to balance the brain hemispheres and nutritional protocols to support healthy brain metabolism.
One of the most important factors in managing any patient case is understanding what the person is experiencing. Analyzing the brain waves helps us objectively determine if there is a neurological cause to the symptoms a person is experiencing.
Balancing a person’s brain waves can be very helpful. We have used it for many years and had great success in ADHD, Autism Spectrum, post-concussion, Migraine Headaches, PTSD, Addiction Management, Memory Management, chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and insomnia cases.
OTHER NEWS ARTICLES

What is Neurofeedback and How It helps Brain Health
Inflammation Can Shrink Your Brain
The Gut-Brain Connection Is Important For Mental Health And More!

Beyond Medicating The Brain: Why We Need a New Approach
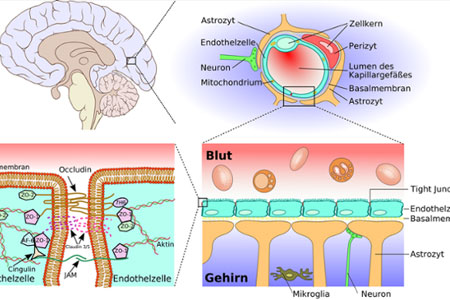
Do You Have A Leaky Brain?

The Seven Types Of ADD

The History Of Neurofeedback And Why It Is Beneficial In Treating ADD And ADHD

Balancing And Nourishing The Brain Helps Resolve Many Health Challenges

Clinic Studies On Neurofeedback – Make An Informed Decision For Drug Free Care

Brainwaves, The Key To Healthy Brain Function
[themify_layout_part id=239]


