Red light therapy, also known as photobiomodulation or low-level light therapy (LLLT), is a therapeutic technique that uses low-intensity red light wavelengths to stimulate various biological processes in the body. It involves exposing the skin or specific body parts to red or near-infrared light.
Red light therapy works by delivering specific wavelengths of light to the cells, which are absorbed by mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within the cells. This interaction with the mitochondria triggers a series of physiological responses, including increased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), enhanced cellular metabolism, and the release of nitric oxide.
The therapeutic benefits of red light therapy include:
- Skin health: Red light therapy has been used to promote skin rejuvenation, reduce wrinkles and fine lines, improve skin tone and texture, and enhance collagen production.
- Pain relief: It has shown efficacy in reducing pain and inflammation, particularly in musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis, joint pain, and muscle soreness.
- Wound healing: Red light therapy can accelerate the healing process of wounds, including cuts, burns, and ulcers, by enhancing cell proliferation and tissue repair.
- Mood enhancement: Some studies suggest that red light therapy may have positive effects on mood and mental well-being, potentially alleviating symptoms of depression and improving overall mood.
- Hair growth: It has been explored as a potential treatment for hair loss by stimulating hair follicles and promoting regrowth.
Red light therapy can be administered through various devices, including light-emitting diodes (LEDs), lasers, or lamps. The treatment duration and frequency can vary depending on the specific condition being targeted, and sessions typically range from a few minutes to 20 minutes or more.
It is generally considered safe, non-invasive, and well-tolerated, with minimal side effects. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist before starting red light therapy, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking medications that may interact with the treatment.
Key Findings and Promising Research on How Red Light Therapy – Photobiomodulation
Research on the use of photobiomodulation (PBM) in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease is still in its early stages, and more studies are needed to establish its effectiveness and therapeutic potential. However, preliminary research and preclinical studies have shown some promising results. Here are a few key findings:
- Improved cognitive function: Several animal studies have demonstrated that PBM can improve cognitive function in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. For example, mice subjected to PBM treatment showed improvements in memory, learning, and spatial navigation tasks.
- Reduction of amyloid beta plaques: Amyloid beta plaques are one of the characteristic features of Alzheimer’s disease. Some animal studies have suggested that PBM may help reduce the accumulation of amyloid beta plaques in the brain, potentially slowing down the progression of the disease.
- Neuroprotective effects: PBM has been found to have neuroprotective effects, meaning it can protect neurons from damage and degeneration. Animal studies have shown that PBM can enhance the survival of neurons and promote neuronal regeneration, which may be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases.
- Modulation of inflammation: Inflammation plays a role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. PBM has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and promoting a more favorable anti-inflammatory environment in the brain.
- Enhancement of mitochondrial function: Mitochondrial dysfunction is believed to contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. PBM has been found to improve mitochondrial function and increase ATP production, which can support cellular energy metabolism and overall neuronal health.
Inflammation and the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease
Inflammation plays a significant role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The brain of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease often exhibits chronic neuroinflammation characterized by increased activation of immune cells and the release of inflammatory molecules. Here are some key points about the modulation of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease:
- Amyloid beta and inflammation: The accumulation of amyloid beta plaques in the brain is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. Amyloid beta can trigger an immune response, leading to the activation of microglia, the resident immune cells in the brain. Activated microglia release pro-inflammatory molecules such as cytokines and chemokines, which contribute to neuroinflammation.
- Tau pathology and inflammation: Another characteristic feature of Alzheimer’s disease is the formation of neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Tau pathology can also trigger an inflammatory response, further exacerbating neuroinflammation.
- Activation of immune cells: In Alzheimer’s disease, microglia and astrocytes, another type of glial cell in the brain, become activated and release pro-inflammatory molecules. This chronic activation and release of inflammatory mediators contribute to neuronal damage and synaptic dysfunction.
- Pro-inflammatory molecules: Various pro-inflammatory molecules are implicated in the inflammation observed in Alzheimer’s disease. These include cytokines (such as interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha), chemokines, reactive oxygen species, and prostaglandins. These molecules can disrupt normal neuronal function and promote neurodegeneration.
- Impact on neuronal health: Chronic inflammation can have detrimental effects on neuronal health. It can lead to oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, and the production of toxic molecules that contribute to the death of neurons and the progressive cognitive decline observed in Alzheimer’s disease.
Targeting inflammation as a therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease is an active area of research.
Red Light Therapy as a Drug Free Approach to Treating Alzheimer’s
Red light therapy may be considered as a drug-free approach for treating Alzheimer’s disease due to several potential advantages:
- Non-invasive and low-risk: Red light therapy is a non-invasive treatment that involves exposing the body or specific areas to low-intensity red or near-infrared light. It is generally considered safe, with minimal side effects or risks when used appropriately. Compared to pharmaceutical interventions, which often carry the risk of adverse reactions and interactions with other medications, red light therapy presents a lower risk profile.
- Potential neuroprotective effects: Preclinical studies have indicated that red light therapy may have neuroprotective effects, promoting neuronal survival and regeneration. This could be particularly beneficial in Alzheimer’s disease, where the progressive loss of neurons contributes to cognitive decline.
- Modulation of inflammation: As mentioned earlier, chronic inflammation plays a role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Red light therapy has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce inflammation in the brain. By modulating inflammation, red light therapy may help mitigate the damaging effects of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Enhanced cellular energy production: Red light therapy stimulates mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within cells. This interaction leads to increased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy source for cellular processes. In Alzheimer’s disease, mitochondrial dysfunction is observed, and enhancing cellular energy production through red light therapy may help support neuronal function.
- Non-pharmacological approach: Red light therapy offers a non-pharmacological approach to Alzheimer’s disease treatment, which may be particularly appealing for individuals who prefer drug-free options or for whom pharmaceutical interventions may be contraindicated or less desirable due to specific health conditions or medication interactions.
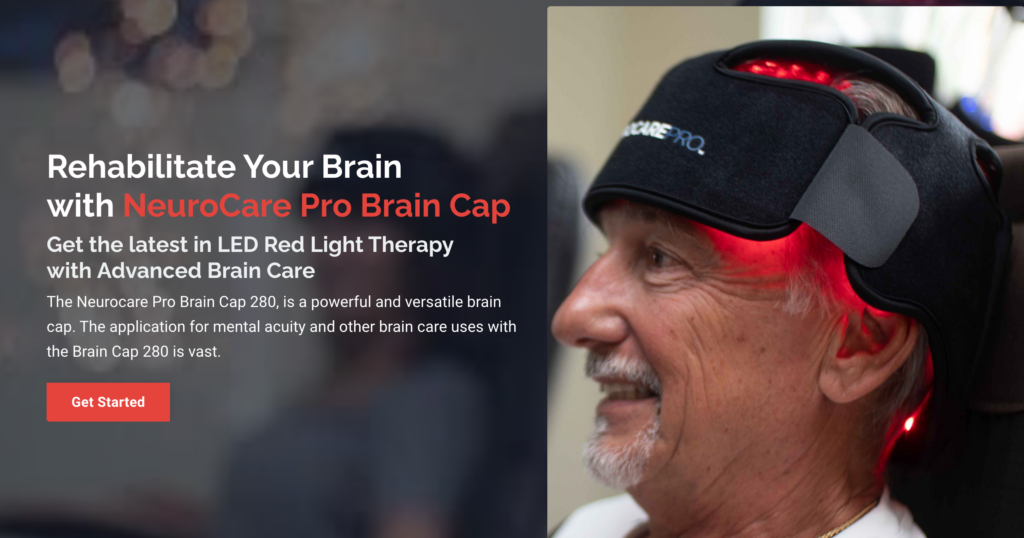
It’s important to note that while red light therapy shows promise, and it’s an emerging field. At Saving Your Brain, we have partnered with Neurocare Pro to offer the latest in brain care technology using photobiomodulation. Patients are able to purchase the Neurocare Pro Brain Cap for continued therapy at home after an initial consultation and individualized treatment plans developed based on specific needs and considerations. Please contact Dr. Kelly Miller, NMD from Saving Your Brain at info@savingyourbrain.com to learn more about the Neurocare Pro Brain Cap or visit this link and complete the form and our support team will get back to you shortly with more details.


